In the early 1990s, mobile phones were just beginning to gain mainstream popularity. However, the ability to connect to the internet was still a distant dream. This all changed with the introduction of 2G networks.
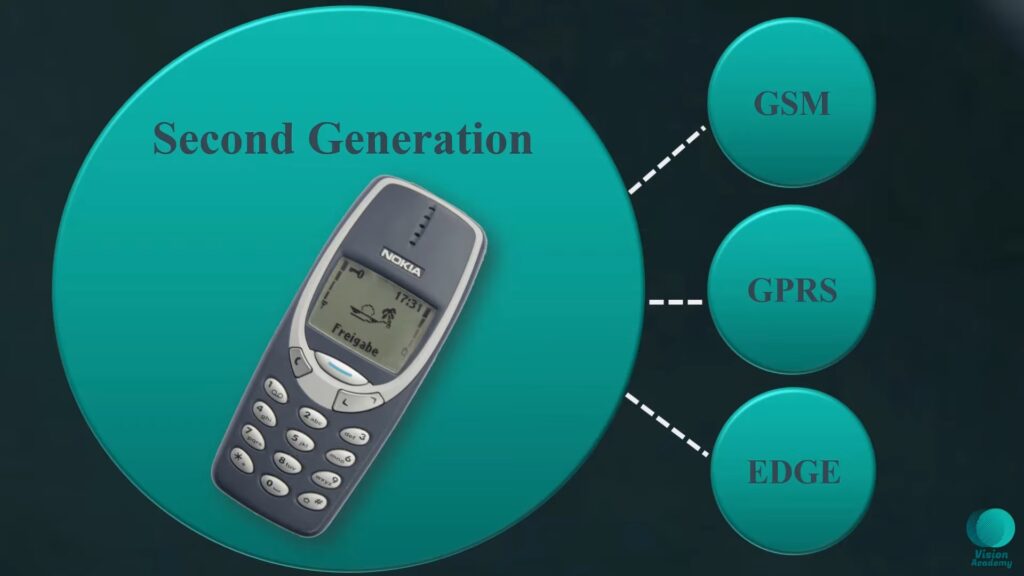
2G networks were the first to introduce digital mobile communication. They replaced the analog systems that had been used up until that point. One of the key advantages of 2G networks was their ability to transmit data at a much faster rate than their analog predecessors. This made it possible to access the internet from a mobile device.
Initially, 2G networks were slow and unreliable, with internet speeds of just a few kilobits per second. However, they were a significant improvement over the previous analog systems, which had no internet connectivity at all.
The first mobile phones with 2G connectivity were released in the mid-1990s. These early devices were simple by today’s standards, with small monochrome displays and limited internet browsing capabilities. However, they laid the foundation for the mobile internet as we know it today.
Over time, 2G networks continued to evolve and improve. The introduction of GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) in the late 1990s made it possible to send and receive data at a much faster rate than before. This paved the way for more advanced mobile internet applications, such as email and instant messaging.
The next major development in 2G networks came with the introduction of EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution) in the early 2000s. EDGE increased internet speeds to around 384 kilobits per second, which was a significant improvement over previous versions of 2G.
The introduction of 2G networks also had a major impact on the telecommunications industry. It paved the way for the introduction of prepaid mobile plans, which made it much easier for people to access mobile communication and internet services.
In addition, 2G networks played a crucial role in the development of mobile banking and financial services. The ability to access the internet from a mobile device made it possible to transfer money, pay bills, and access other financial services from almost anywhere.
However, the limitations of 2G networks soon became apparent. As internet usage on mobile devices increased, it became clear that 2G networks were not able to keep up with demand. Internet speeds were still slow, and it was difficult to access more advanced mobile applications and services.
This led to the introduction of 3G networks, which were able to transmit data at a much faster rate than 2G networks. 3G networks paved the way for more advanced mobile applications, such as video calling, mobile gaming, and high-speed internet browsing.
Despite their limitations, 2G networks played a crucial role in the development of mobile internet technology. They paved the way for more advanced systems, such as 3G and 4G, and laid the foundation for the mobile internet as we know it today.
The introduction of 2G networks was a major milestone in the history of internet speeds. They were the first mobile networks to introduce digital communication, which made it possible to access the internet from a mobile device. While they were slow and unreliable by today’s standards, they were a significant improvement over the previous analog systems. The introduction of 2G networks paved the way for more advanced mobile internet technology, and laid the foundation for the mobile internet as we know it today.