The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has opened up a world of possibilities for various industries, including transportation. IoT-enabled transportation systems utilize connected devices, sensors, and data analytics to revolutionize the way people and goods move from one place to another. In this article, we will delve into the benefits, challenges, and future trends of IoT-enabled transportation systems.
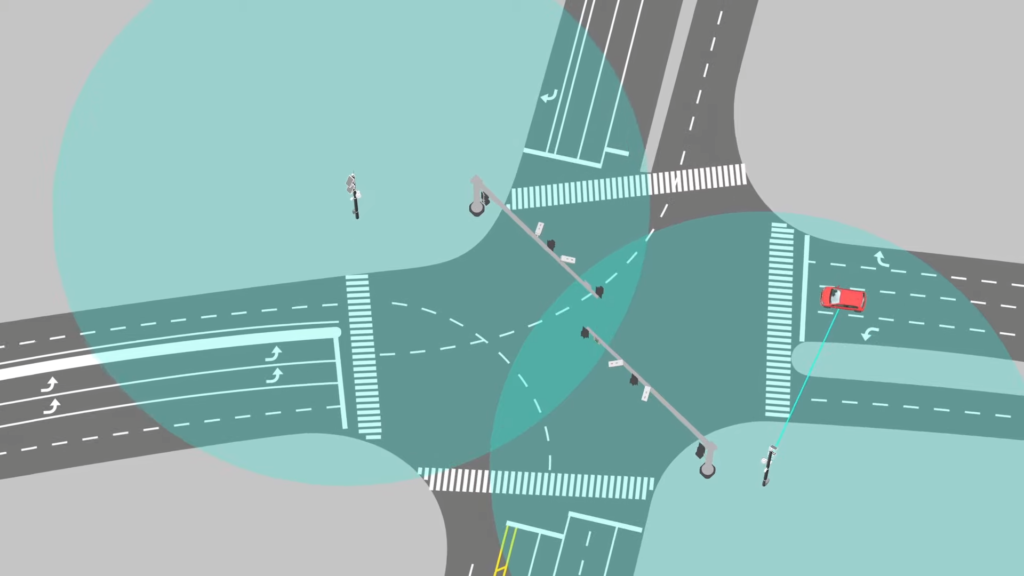
Benefits of IoT in Transportation
- Improved Efficiency: IoT enables real-time monitoring and optimization of transportation systems. Sensors installed in vehicles, traffic lights, and infrastructure gather data on traffic flow, congestion, and road conditions. This information allows for efficient route planning, traffic management, and congestion reduction, leading to smoother and faster transportation.
- Enhanced Safety: IoT-enabled transportation systems enhance safety by providing real-time monitoring and analysis of vehicle conditions. Sensors can detect issues such as tire pressure, engine performance, and driver behavior, allowing for proactive maintenance and timely interventions. IoT also enables intelligent traffic management systems that can detect accidents or hazards and alert relevant authorities.
- Smart Parking Solutions: IoT can optimize parking management by providing real-time information about available parking spaces. Sensors installed in parking lots and on-street parking spots can relay information to drivers through mobile applications, reducing the time spent searching for parking spaces and alleviating congestion in urban areas.
- Efficient Fleet Management: IoT enables fleet operators to track and manage vehicles more effectively. Connected devices collect data on vehicle performance, fuel consumption, and driver behavior. This data helps optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance maintenance scheduling, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
- Seamless Intermodal Connectivity: IoT facilitates seamless integration and connectivity between different modes of transportation. Through interconnected systems, passengers can plan and book multimodal journeys, leveraging real-time data on public transportation schedules, availability of shared bikes or scooters, and ride-sharing options. This integration encourages the use of sustainable and efficient transportation modes.
Challenges of IoT in Transportation
- Data Security and Privacy: The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices in transportation systems raises concerns about data security and privacy. Safeguarding sensitive information, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations are critical challenges that need to be addressed.
- Interoperability and Standardization: IoT-enabled transportation systems involve various stakeholders, including vehicles, infrastructure, and service providers. Achieving interoperability and standardization among these diverse components is essential to enable seamless communication, data sharing, and integration. Industry-wide collaboration is necessary to develop common protocols and standards.
- Infrastructure Requirements: IoT relies on robust and reliable network infrastructure to support the transmission of data between connected devices. Expanding high-speed internet coverage, deploying wireless communication networks, and ensuring adequate bandwidth are essential for the widespread adoption of IoT in transportation.
- Scalability and Integration: As the number of connected devices increases, ensuring scalability and seamless integration becomes challenging. Transportation systems need to accommodate the growing volume of data, handle real-time analytics, and support interoperability between different devices and platforms.
Future Trends in IoT-Enabled Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles: The rise of autonomous vehicles will significantly impact IoT-enabled transportation systems. Connected autonomous vehicles will communicate with each other and with traffic infrastructure to optimize traffic flow, enhance safety, and reduce congestion.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source rather than relying on a centralized cloud, will become more prevalent in IoT-enabled transportation systems. Edge computing allows for real-time data analysis, faster response times, and reduced dependence on cloud connectivity.
- 5G Connectivity: The deployment of 5G networks will provide ultra-fast and low-latency connectivity, unlocking new possibilities for IoT-enabled transportation systems. It will enable real-time data exchange, support a massive number of connected devices, and enhance the reliability of critical applications.
- Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning: IoT-generated data combined with predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms will enable transportation systems to anticipate traffic patterns, optimize routing, and improve resource allocation. This data-driven approach will lead to more efficient and intelligent transportation networks.
IoT-enabled transportation systems offer numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced safety, smart parking solutions, efficient fleet management, and seamless intermodal connectivity. However, challenges such as data security, interoperability, infrastructure requirements, and scalability need to be addressed. Looking ahead, the future of IoT in transportation holds promises of autonomous vehicles, edge computing, 5G connectivity, and advanced analytics. By embracing these trends and addressing the challenges, we can build a more connected, efficient, and sustainable transportation ecosystem.